Distended Bladder
What is Distended Bladder?
Distend bladder means when urinary bladder is full, but sufferer cannot pass the sufficient amount of urine and causes lower abdominal pain. In this condition, sufferer has feeling for passing urine, but cannot release urine or pass very little urine, which is not sufficient to give relief from the urge. For which sufferer always have feeling of full bladder and tends to pass urine.
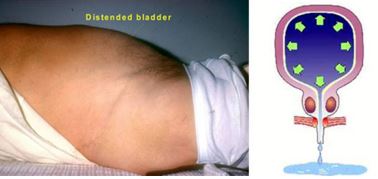
Image 1: Distended Bladder
Symptoms
The following symptoms are associated with distended bladder:
- Pain in the lower abdomen. The usual symptom of the distended bladder is pain in the lower abdomen. Gradually the lower the navel potion of the abdomen gets tendered which can feel by touching. Lower abdomen gets tough and tensed. In initial stage, the pain is more intense than in chronic condition.
- Micturition difficulty: Sufferer cannot release urine even in cases of bladder is filled up. During urination strain is developed in the outlet and burning sensation is very frequent. The patient has the urge to release the urine, but unsatisfied result occurs due to partial urine release.
- Frequent to go for urination: Partial release of urine increases the time frequency to go for urination.
- Increase time duration of micurition: The urine flow is not smooth and prolongs time is required to pass, even after the partial urination strain is sustained in the outlet.
- Bilateral pedal oedema means fluid retention causes swelling of the feet.
- If this associated with neurological disorder, then numbness, pinning sensation in the limbs and muscular weakness are common.
- Fever is often associated because of infection develop.
Causes
Broadly, distended bladder occurs due to the following reasons:
- Obstruction in the passage of urine release
- Neurological disorder which leads to problematic micturation (urination process)
- Sphincter spasticity
The following are the identified disorder which causes obstruction in the urinary pathway
- Stone formation in the urinary bladder, which obstructs the urine passage and causes retention of urine in the bladder.
- Prostate gland enlargement which blocks the urethra (the outlet of the urine) and urine retain in the bladder itself. It is very common in older male individuals. The distension of the bladder depends upon the size of the prostate gland and may partially or fully block.
- The urine outlet (urethra) which is attached with urinary bladder and during urine releases, it’s open and passes the urine. If the urethra gets infected, structural deformity, ulceration or spastic condition leads to spasm and hamper the urine release.
Neurological syndrome – Bladder wall contraction and relaxation is controlled by spinal nerves and degeneration of these nerves cause abnormalities in the bladder wall contraction and relaxation. Usually this condition arises with spinal cord degeneration, which may occur due to rigidity in the spine, tumour formation in the spine or accidental injury in the vertebral column.
Pott’s disease which is an infection caused by tuberculosis and affects vertebral disc and causes contraction in the spinal nerves, followed by nerve compression and problematic contraction and relaxation of the bladder.
Genital organ diseases like ovarian tumour, pelvic cyst or uterine fibrosis causes distended urinary bladder in females.
Some drugs like muscle relaxants, anaesthetics and antihistamines can develop bladder enlargement and lead to distended bladder.
Diagnosis
The physical examination is important to check the condition.
- When palpated the usual finding is inflamed lower abdomen.
- Physical examination helps to find muscle of the lower abdomen become tightened than the usual and become tender and increase strain.
- Usually blood pressure is increased due to fluid retention.
- The distinctive cystometrogram result of cauda equina injury is detrusor areflexia. An abdominal straining and saw tooth pattern is generally seen in the uroflowmetry.
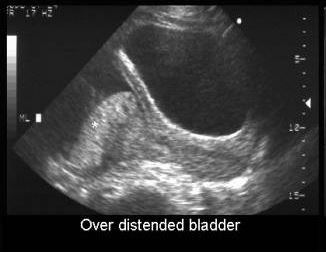
Image 2: Ultrasonography of distended bladder
Treatment
- Hearing of flow of water from tap often initiate the urine release.
- Hot compression able to relief the pain and distension. It also helps to release the urine and associated tenderness become lessens.
- In case of tuberculosis infection or pott’s disease, antibiotic medications treat the tuberculoisis and symptomatic relief can occur.
- In hospital, catheterization is one of the options to release the urine completely. It is applied in emergency and severe cases. Precautionary measures like subsequent aseptic techniques are important to control the urinary tract infection.
- Biofeedback is another treatment method which can help patient by giving proper guidance about how to control the sphincter contraction and relaxation to facilitate micturition. In computer monitor, improvement can be detectable.
- Bethanechol chloride is available medication to treat the balder detention as it stimulates parasympathetic nerves to regulate the normal contraction and relaxation of the sphincter muscle during urination.
- Sphincter spasticity can be treated by botulinum toxin injection.
- Advancement of medical science develops a novel medical device which has to implant inside the body in case of neurological disorder. This device able to stimulate involved nerves and muscles situated at the bladder and regulate the normal contraction and relaxation for micturition.
References
- What Causes Distended Urinary Bladder: Its Symptoms And Treatment at http://www.simple-remedies.com/health-tips-6/distended-bladder-causes-treatment.html
- Distended bladder presenting with constipation and venous obstruction: a case report at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3398309/
- http://www.wisegeekhealth.com/what-is-a-distended-bladder.htm
- Distended Bladder Causes of Outlet Obstruction in Men and Women at http://www.healthhype.com/distended-bladder-causes-of-outlet-obstruction-in-men-and-women.html
- http://www.livestrong.com/article/146979-distended-bladder-symptoms/
- Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Impaired Bladder Emptying at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1472851/
