Metrorrhagia
Metrorrhagia Medical Definition
Metrorrhagia is an unusual bleeding in females that occur between periods. It is not associated with normal menstrual bleeding. Many women call this condition spotting1.

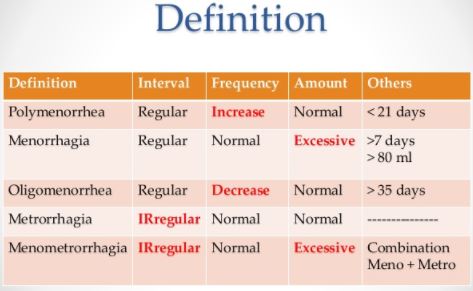
What is Menstrual Period?
Menstrual cycle is the time between the first day of bleeding and the next first day of bleeding. Menstrual cycle is a regular process controlled by hormones and ovulation. On average, the menstrual cycle takes 28 days but it varies among different individuals; in some females it may be longer while in others short. The cycle may take between 21-35 days in different females.
Every month, the uterine wall of a female becomes thick as it accumulates extra blood in preparation of a potential fertilized egg. When an egg is fertilized by the sperm, it implants itself on the uterine wall, develops into an embryo, fetus and then the baby. While on the other hand, the egg which is not fertilized does not implant in the uterine but it is removed through menstrual bleeding.
During menstruation cycle, a hormone-like substance called prostaglandins triggers the uterine to contract. The uterine walls shed blood which is removed through the vagina.2
Metrorrhagia Causes
Metrorrhagia can be caused by numerous factors such as:
Imbalance in hormones
Menstruation period is controlled by hormones. The most known hormones for this process are estrogen and progesterone. These hormones are produced by the ovaries and pituitary gland. Estrogen is responsible for stoping the production of FSH hormone by the pituitary gland so that only one egg matures during menstruation period. It also stimulates the pituitary gland to release LH hormone which makes the matured egg to be released by the ovary. Progesterone is produced by the ovaries and is used to maintain the uterine lining throughout the pregnancy.
When there is very low production of progesterone and too much estrogen secreted, it creates an imbalance in hormones. This imbalance in hormones estrogen and progesterone may cause abnormal bleeding.
Anovulation
This is where a woman skips ovulating. Normally, during ovulation, a woman produces an egg. The Progesterone hormone release is triggered by the egg and it helps a woman keep the regular periods. However, during anovulatory cycle, the ovarie release little progesterone hormones which may cause heavy bleeding. This is not normal bleeding as most women may think.6
Thyroid disorders
These are conditions that affect the thyroid gland. A thyroid gland is a butterfly like organ found in the neck. It is used to produce thyroid hormones that control metabolic processes in the body.
These disorders may affect the function or the structure of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is controlled by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland found in the brain.
The following are some thyroid disorders:
Hypothyroidism
This condition occurs when thyroid gland secretes little thyroid hormones. Hypothyroidism can result from problems in the thyroid gland, pituitary gland or hypothalamus. Some of the common causes of hypothyroidism include Hashimoto’s thyroiditis; it is an autoimmune disorder that causes the thyroid gland to become inflamed. Other causes include acute thyroiditis and postpartum thyroiditis which contributes to the inflammation of the thyroid gland.
Hypothyroidism may cause excessive or prolonged bleeding in women. It may also lead to fatigue, joint and muscle aches as well as depression.
Hyperthyroidism
This condition is characterised by excess production of thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism raises the rate of metabolism. It can be caused by too much Iodine in the body.
Ovarian cysts
Ovaries are female reproductive organs. They are found in the lower abdomen on both sides of the uterus. Women have two ovaries which secrete an egg as well as progesterone and estrogen hormone. In some cases, a fluid-filled sac may form on one of the ovaries; this is known as a cyst. Cysts may not be painful and most women may have at least one during their lifetime.4
Infections
There are various vaginal infections and of one of them is vaginal infection. Vaginal infection is caused by yeast called Candida. Vaginal infection is also referred to as Candidal vaginitis, or Candidal vulvovaginitis.
Candida are present in women vaginas and do not cause problems. For an infection to occur, the normal population of yeast and bacteria in the vagina should be disrupted. This allows yeast to reproduce and become more in the vagina leading to an infection. Yeast can spread through sexual intercourse but Candidal vaginitis is not considered a sexually transmitted infection.
Vaginal yeast infection can occur due to some medications that affect the population of bacteria and yeast in the vagina. Antibiotic and immunosuppressive drugs can cause yeast to multiply which in turn attack the vaginal lining leading an infection.
Injury to the vaginal lining especially after cancer treatment procedures such as chemotherapy can cause an infection.3
Other Causes
Other causes of metrorrhagia include:
- A miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy which is growing in the wrong place in the fallopian tubes.
- Fibroids or tumors which form in the uterine lining may also cause this condition.
- Injury to the vaginal lining or cervix during sexual intercourse may cause bleeding.
- Use of birth control devices such as an intrauterine device may disrupt the bacteria and yeast populations in the vagina which leads to an infection.
- Blood clotting disorders may also lead to abnormal bleeding between periods in some women.
- Use of blood clotting drugs may cause metrorrhagia.
Metrorrhagia Symptoms
The most common symptom of metrorrhagia is where a woman experience light to heavy bleeding between normal bleeding. Other symptoms include pain in the abdomen and cramps. In case of miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy, you will experience severe pain in the abdomen and cramps.2
Diagnosis
There are various methods and tests that can be used to diagnose metrorrhagia. They include: 1
- Physical exam: In this exam, your doctor discusses with you your health record and assesses your symptoms.
- Cultures: Your doctor may perform pelvic examination where cultures of organs in the abdomen are taken and analyzed for infections.
- Blood test: Your doctor will take a sample of your blood and test hormone levels.
- Pap smear. Your doctor may also conduct Pap smear test to check for cervical cancers.
- Ultrasound: Your doctor will place an ultrasound device on your lower abdomen or in the vagina. This device produces sound waves which are used to create pictures of your reproductive organs.
- Biopsy: Your doctor may take a sample of tissue in the uterine to check for abnormalities and hormonal imbalances.
Treatment
Metrorrhagia can be successfully managed when underlying causes are treated effectively. Treatment options depend on the cause and they include1:
- Surgery is used to treat polyps, fibroids and cancer cells in the uterine. Cancer can also be treated using radiotherapy, chemotherapy or a combination of other treatment options.
- Medicines can be used treat infections such as antifungal drugs to cure yeast infections.
- Removal of birth control device is also recommended.
- In case of miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy, dilation is used to eliminate the remaining tissues.
Reference list
- Metrorrhagia http://www.babymed.com/metrorrhagia-irregular-spotting-or-bleeding-between-menstrual-periods
- Metrorrhagia https://www.diagnose-me.com/symptoms-of/metrorrhagia.php
- Metrorrhagia http://firstaidhalifax.ca/causes-symptoms-treatment-metrorrhagia/
- Ovarian Cysts http://www.healthline.com/health/ovarian-cysts#overview1
- Thyroid disorders http://www.medicinenet.com/thyroid_disorders/article.htm
- Anovulatory Cycle http://www.healthline.com/health/pregnancy/anovulatory-cycle
