Left Testicle Pain
Left Testicle Pain Introduction
Testicles are male genital organ and too much sensitive toward any type of pain stimuli. Testicles pain or discomfort can arise with various causes associated with or without swelling. Sometimes an injury may not be present within the testicles, but disorder associated with adjoin coiled tube, scrotum, epididymis (tissues present at the back of the testicles), groin or even distant part from testicles, such as lower abdominal pain due to kidney stone, inguinal hernia also can produce pain in the testicles.
Causes of Left Testicle Pain
The possible underlying causes are:
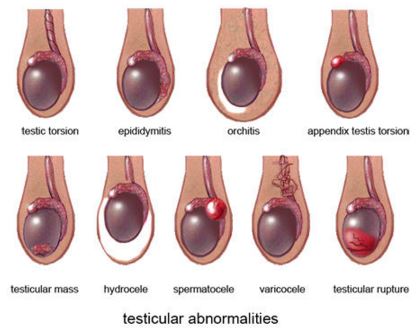
Image 1: Causes of testicular pain
Testicular torsion
This is the condition when the attachment of the testicle within the scrotum gets twisted and mostly affects left sided testicle. The abnormality of the attachment cause pain and it is more often occurs in the neonatal and the adolescent age. The incidence rate is low after 30 years of age.
Medically termed as retractile testicle can be explained as the affected testicle tow up inside the groin, it is mostly occurs in younger aged children.

Image 2: Testicular torsion
Blood vessels, nerves, lymphatic vessels injury
Blood vessels, nerves, lymphatic vessels are attached with spermatic cord. Any injury or disease conditions such as Henoch-Schonlein purpura, diabetic nephropathy which hamper the blood supply, block the lymphatic drainage or nerve damage causes pain and discomfort within the testicles.
Vericocele is the condition where the veins of testicle become enlarged and generate pain.
Fluid accumulation
Fluid accumulation in the scrotum occurs in hydrocele and spermatocele causes fluid retention inside the testicles. Both the disease conditions cause pain and discomfort in the testicles.
Inflammatory condition developed in testicles
Testicles inflammatory conditions arise with several diseases like epididymitis, orchitis. These diseases cause testicles pain and discomfort.
Infection
Bacterial and viral infections in the tissues of testicle cause testicles pain. The mumps virus is one of the infecting viruses which can affect testicle. Urinary tract infection also causes testicular discomfort. In case of severe bacterial infection and remain untreated, causes Fournier’s gangrene, where testicular tissues become necrotic. Sexually transmitting infections like Gonorrhoea or Chlamydia cause pain in testicles.
Vasectomy
Vasectomy is a male surgical process to control the birth and completely safe. But 6% of men complaining pain in testicles after vasectomy, yet the exact medical explanation does not obtain about the generation of the pain after vasectomy.
Malignancy
Malignant cell proliferation in the testicular cancer causes pain.
Unknown cause or Idiopathic testicular pain
Some time the reason behind the testicular pain or discomfort is unknown.
Associated Symptoms
Other than the pain and discomfort feel in the testicles, associated symptoms which developed due to underlying causes are as follows:
- Inflammation may or may not be present depending upon the underlying disease conditions.
- Redness
- Fever
- The nature of pain is dull
- Throbbing sensation is present
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Pain in lower abdomen
- Associated discomfort become high in day time
- Clothing, touching even bed cloths worsens the condition in severe cases
- Position of affected testicle is raised up inside the scrotum.
Differential Diagnosis
To understand the underlying cause laboratory diagnostic and imaging techniques help to diagnose.
Laboratory tests
The blood tests and urine analysis are common laboratory tests conducted to know the underlying disease condition. If any urethral discharges are present, doctors suggest to conduct the test of the discharged fluid in the laboratory.
Blood test
- Usually total blood count, Erythrocytes Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-protein level is checked.
- Total Blood Count (CBC) is often helps to estimate the chances of infection.
- ESR and C-protein analysis also help to identify inflammatory condition.
Urine analysis
Routine urine analysis helps to estimating the infection and urine culture often identify the causative microorganisms.
Urethral discharge
In case of sexually transmitting diseases, analysis of urethral discharge helps to identify the causative organism.
Imaging techniques
Ultrasound
Ultrasonographic test for testicles helps to determine blood circulation obstruction, tumour formation, fluid retention, damage in testicles and hernia development. Lower abdominal ultrasound helps to analysis the kidney stone.
Radionuclide imaging
To understand the testicular torsion, radionuclide imaging test may conduct where ultrasounds are not providing proper view.
KUB (kidney/ureter/bladder X-ray) or/ and CT scan
If the very minute stone is present in kidney cortex and cannot view or doubtful view is obtained by ultrasound then KUB or CT scan is conducted for confirmation.
Left Testicle Pain Treatment
The general treatments for any cause of development of pain in testicles are,
- Adequate rest
- Cold, ice compression
- Analgesic medications for reduction of the pain
- Scrotal support
Other than the above mentioned general treatment, following specific treatment options is also followed:
- Antibiotics are prescribed for infective condition
- Plenty of water and fluid intake is suggested for kidney stone
- Prompt Surgery is recommended in case of testicular torsion, inguinal hernias and tumour development
- Chemotherapy or radiotherapy prescribed in case of testicular cancer.
References
- What is the treatment for testicular pain? at http://www.medicinenet.com/testicular_disorders/page6.htm
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/testicle-pain/basics/when-to-see-doctor/sym-20050942
- Painful testicle(s) with or without swelling at http://www.embarrassingproblems.com/problem/testicle-problems/painful-testicle
- http://www.emedicinehealth.com/testicular_pain/article_em.htm
- Testicle Pain: Causes, Complications, & Treatment at http://www.healthline.com/symptom/pain-in-testicle
